Which problems does ML solve?
Contents
Which problems does ML solve?#
Machine learning is used in numerous areas and has invaded our day-to-day life. Whether a search engine on internet ranks website URLs from input keywords, or a camera detects faces or smiles from an image, or online stores lists recommended products to consumers, machine learning is here behind the scene. It takes data in, got trained at the task (the experience E) with ideally lots of data. After evaluations and tests, it can be ready to take new (unknown) data and output a set of predictions. We will review these steps more in detail during the course for each specific algorithm.
Input and output#
As seen from the three examples above, the input data varies: it could be words (string of characters), images (a collection of pixels) or a list of strings and/or numbers (products bought in the past, positions and directions of the produced particles in a detector, etc).
The output too are of different forms. It could be a binary or categorical variable: is this tumor benign or malignant, is this a cat or a dog (it’s a classic example you will see more than enough on the web). It could be numerical value or set of values, for instance the amount of medical kits to send for a given humanitarian disaster.
Definition 2
A classification problem refers to situations where the output is restricted to a limited set of values, in other words classes.
A regression problem refers to situations where the output may have any numerical value within a range.
More subtle outputs are those where there is no target variable but rather a new information learned from the data. Clusters for example. So-called clustering algorithms sort the dataset into groups showing homogeneity. This is widely used by social media companies to build profiles of users (with or without good intentions). In biology and medicine, it can help partitioning patients to adapt treatments for each group. Another type of output is the selection of several data points, or items, deemed too rare with respect to the standard from the entire dataset. They are outliers, or anomalous. The algorithm behind it is called anomaly detection. It is used to detect fraudulous transactions or in the case of particle physics, it could be handy to spot very rare processes.
Approaches#
There are several approaches in machine learning, the principal ones being:
Supervised learning: the training data contains labels, i.e. the real target variable or output. In other words the ‘right answer’ (for instance each picture is labelled ‘dog’ or ‘cat’ in the case of a classification problem, or the price, age, mass in the case of a regression problem).
Unsupervised learning: the training data has no labels. It has only the input. The algorithm’s performs a grouping or clustering or spots anomalies.
Reinforcement learning: the algorithm an agent learns a behavior given an observation in an environment. The action produces a return value in this environment that can be transcribed as a reward the algorithm seeks to maximize.
The latter definition can be confusing. Here is an example: self driving cars. The agent is the self-driving car. By actions we have accelerating/braking and turning left or right. The reward comes from good decision (the car is trained either with a human correcting the actions or in a simulator). Reinforcement learning can also be seen as a form of self-supervised learning.
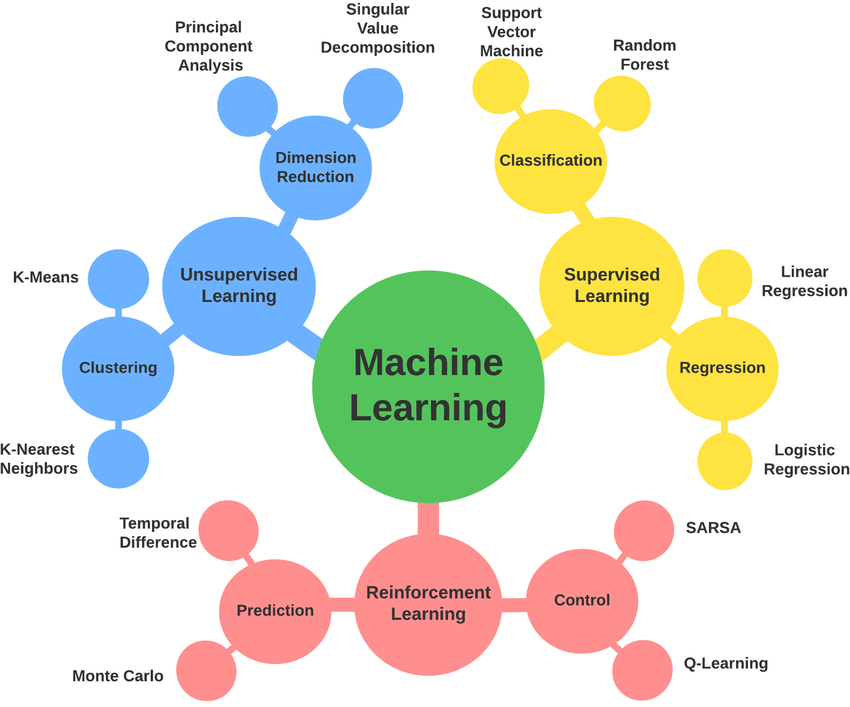
Fig. 8 . A categorization of major machine learning techniques with relevant examples.
Credits: from this publication by Koblah, David & Acharya, Rabin & Dizon-Paradis, Olivia & Tajik, Shahin & Ganji, Fatemeh & Woodard, Damon & Forte, Domenic. (2022). A Survey and Perspective on Artificial Intelligence for Security-Aware Electronic Design Automation. CC BY 4.0#
Examples#
This is left as an exercise for you!
In groups, list several machine learning examples you know of. For each of them:
What are the task, the experience and possible metrics for performance?
What are the data input, the output target(s) if any?
What are the potential benefits and dangers of such algorithm?
How ethical is it?
