What is Ensemble Learning?
Contents
What is Ensemble Learning?#
Definition#
Definition 49
An Ensemble Learning is a technique consisting of aggregating the predictions of an Ensemble, i.e. a group of predictors.
An Ensemble Learning algorithm is called an Ensemble method.
The more diverse the predictors within the ensemble, the better to obtain an accurate final prediction. The fascinating part: the global prediction not only outperforms each individual learners, but the predictors do not have to be that good for this to work. We refer to a not-so-good predictor as a weak learner. Once combined, the ensemble method can generate higher accuracy in the final prediction: it has become a strong learner.
How are the individual results from the predictors combined?
How results are combined#
For regression, taking the average of the predicted values is the most natural way.
For classification, the aggregation is done either through a counting of votes, i.e. which class receives the most predictions (each predictor produces one vote). Or via probability if the predictors provide this information along with the predicted class: the prediction associated with the highest probability wins.
Definition 50
When the combined result of an Ensemble method is done by:
counting the class that gets the most votes among the predictors, i.e. a majority-vote aggregation, we call this is a hard voting classifier.
choosing the class that comes with the highest associated probability (provided the information is available): this is a soft voting classifier.
The hard voting could appear advantageous, it is however impossible to know how confident each vote is, whereas the soft voting benefit from that information. Soft voting thus performs generally better.
There is another concept important in ensemble learning: bagging.
Bagging and Pasting#
Remember that in ensemble learning, diversity is key. Yet it can be impractical to train very diverse learners, each having their own specificities and drawbacks to pay attention to. An alternative approach is to deal only with one algorithm but increase the diversity in the dataset. Like shuffling a deck of cards, bagging involves training predictors on randomized subsets of the dataset.
Definition 51
Bagging, short for bootstrap aggregating, is a method in ensemble learning consisting of resampling multiple times the dataset with replacement, i.e. the procedure can select a data point more than once in a resampled dataset.
Pasting refers to a similar protocol but without replacement (no repeated data points).
Recall the instability characteristic to decision trees. By varying the dataset multiple times, such instabilities are averaged out by all other predictions. In the end, even if each predictor is more biased (due to a given sampling), the aggregated results reduce both bias and variance.
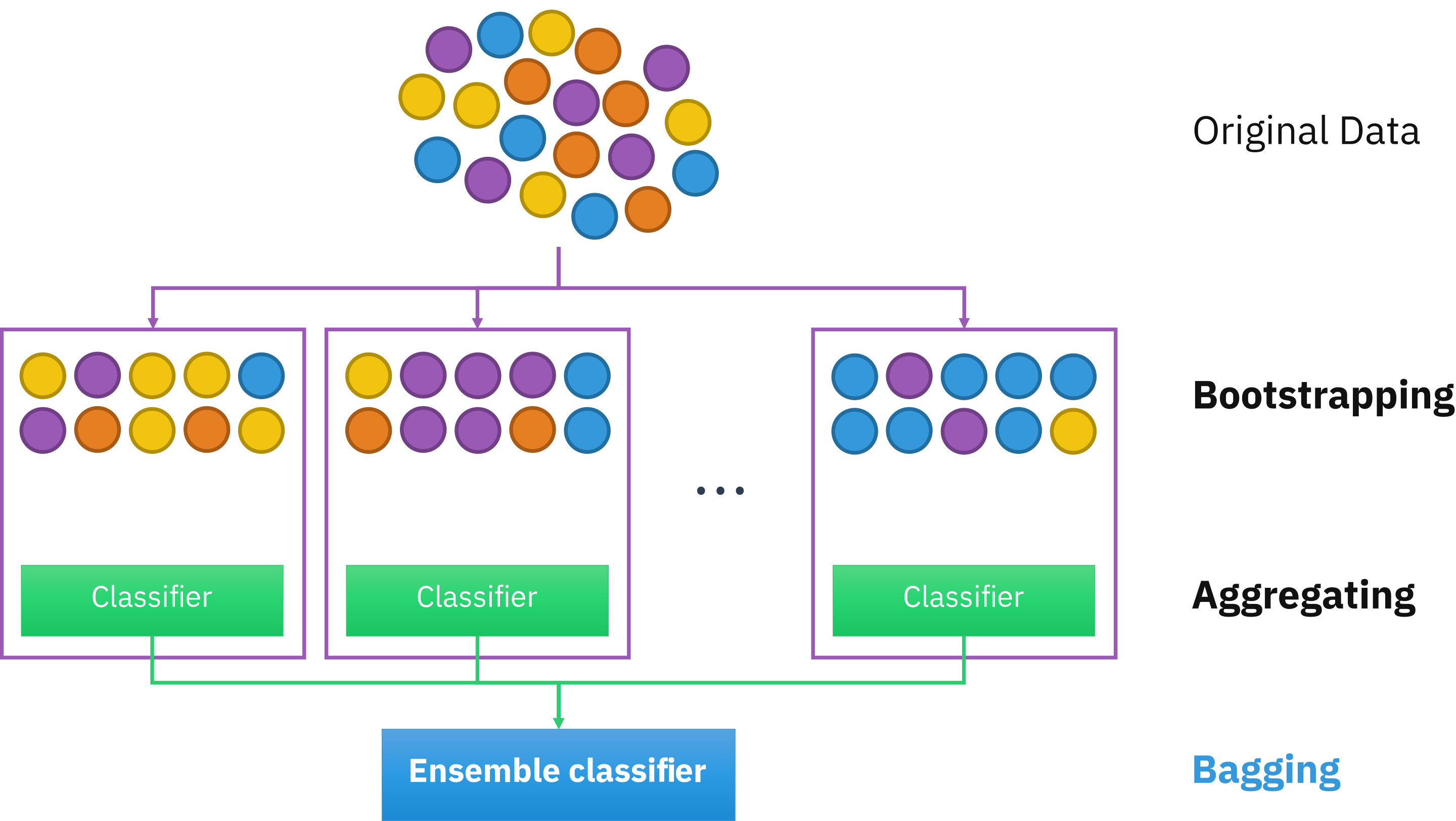
Fig. 27 . Visual of bootstrap aggregating or bagging.
Source: Wikipedia#
Excercise
How do we know from the picture above that it is bagging and not pasting?
So far we have said nothing from the type of predictors. Let’s see a particular example of ensemble method whose predictors are decision trees. The name follows naturally: it’s a forest.
